Earwax impaction is a common but often misunderstood condition. Learn what causes it, how to recognize the symptoms, and the safest ways to remove it - without risking damage to your ears.
Read More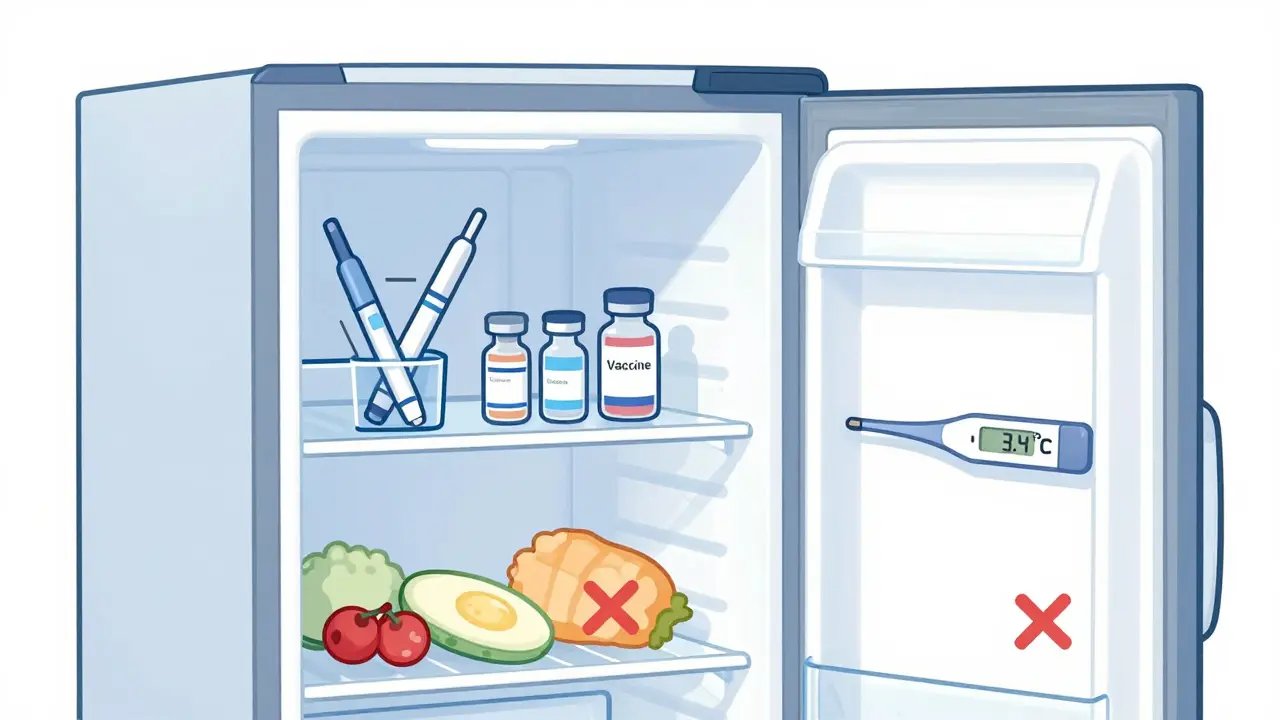
Learn how to properly store refrigerated medications like insulin, vaccines, and biologics at home. Avoid common mistakes, understand temperature ranges, and use simple tools to keep your meds effective and safe.
Read More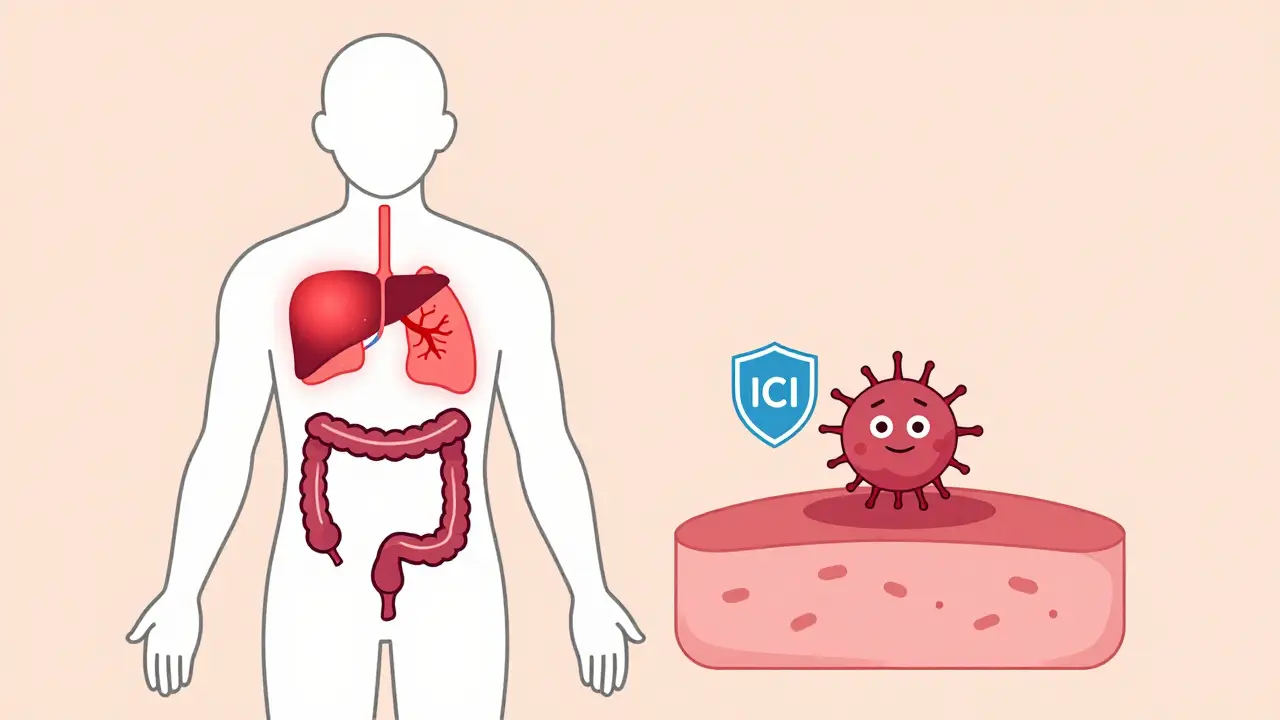
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are common side effects of cancer immunotherapy that can affect any organ. Learn how to recognize, grade, and treat them with corticosteroids and other therapies - and why early action saves lives.
Read More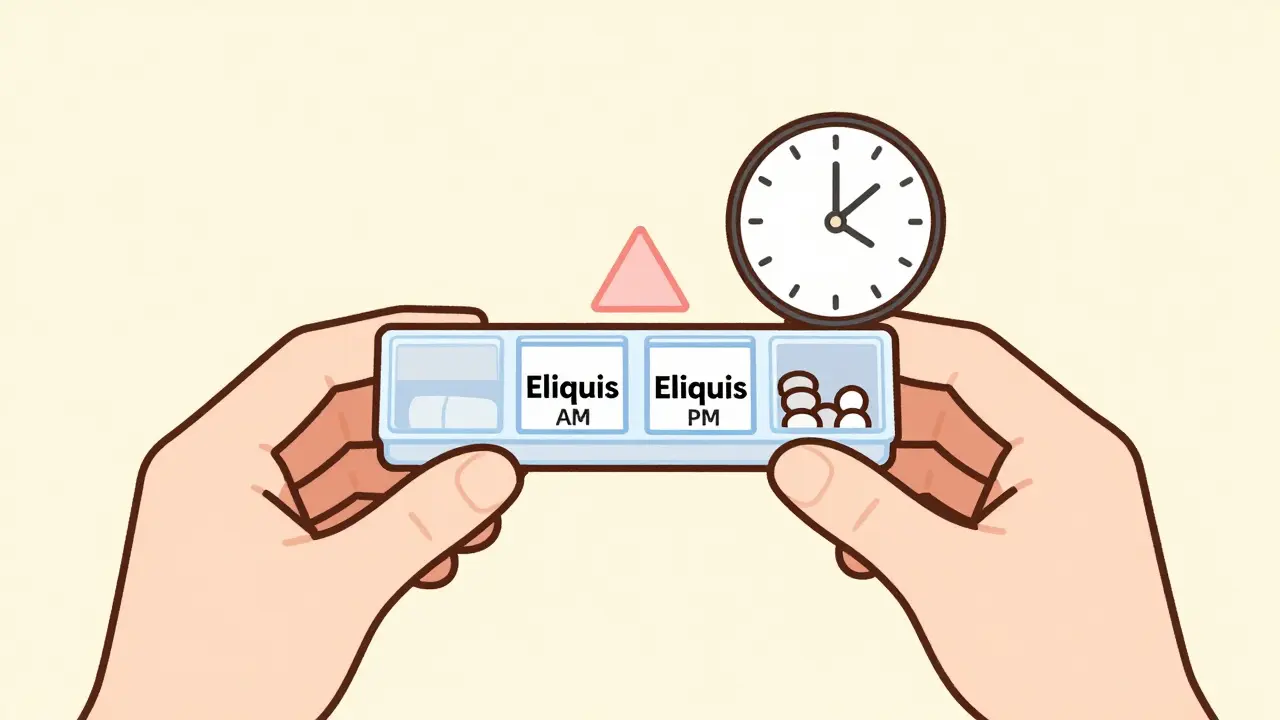
Missing a blood thinner dose can raise your risk of stroke or dangerous clots. Learn what to do if you forget your warfarin or Eliquis, when to call your doctor, and how to prevent missed doses for better safety.
Read More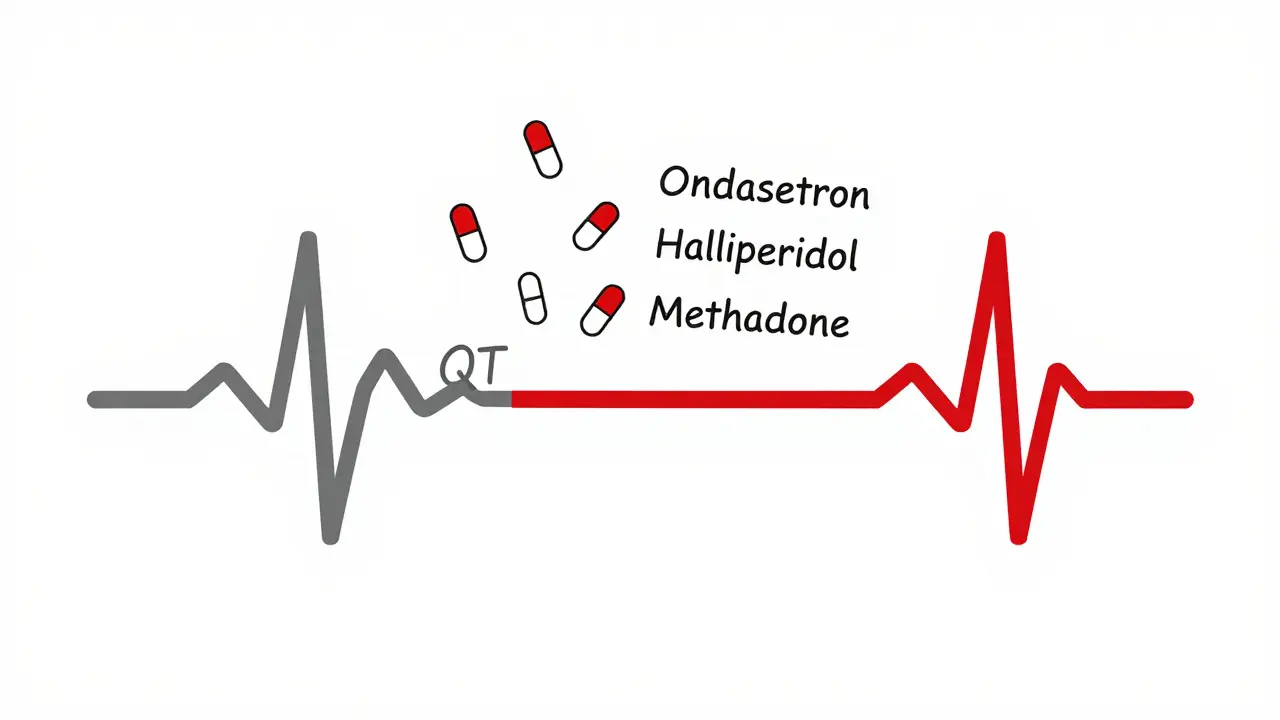
QT prolongation can trigger life-threatening arrhythmias. Many common medications - from antibiotics to antidepressants - can cause it. Learn which drugs raise the risk, who’s most vulnerable, and how to stay safe.
Read More
Heart attack warning signs vary but often include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, and cold sweats. Recognizing these symptoms quickly is critical-delaying care can be fatal. Women and older adults may experience different symptoms than men. Immediate action, like calling emergency services, saves lives. Learn how to act fast during a heart attack emergency.
Read More
A multilingual medication list is essential for emergencies. Learn how to create and maintain one in multiple languages to prevent errors, reduce ER wait times, and ensure clear communication with healthcare providers during crises.
Read More
Generic drugs save billions globally, but availability and pricing vary wildly between countries. Why does the same pill cost six times more in the U.S. than in the U.K.? And why do some generics cause side effects others don't?
Read More
DRESS syndrome is a rare but deadly drug reaction that causes fever, rash, organ damage, and eosinophilia weeks after taking medication. Early diagnosis saves lives-know the signs, triggers, and how to prevent it.
Read More
Pediatric safety networks bring together hospitals and communities to track side effects in children more effectively than traditional studies. These collaborative systems have changed how drugs and treatments are tested, making pediatric care safer through real-time data sharing and adaptive protocols.
Read More